z-index主要控制元素的堆疊順序,決定哪個元素會顯示在最上面,
不過z-index只有在有設定position為relative、absolute、fixed或sticky的時候才會生效。
接下來就是z-index的數值設定啦~正數、負數:數字越大,顯示在越上方。零或auto:為默認值,根據文檔順序堆疊。
以下為範例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Z-Index Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
}
.box1 {
background-color: lightpink;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
z-index: 1;
}
.box2 {
background-color: lightblue;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
z-index: 3; /* 最上層 */
}
.box3 {
background-color: lightgreen;
top: 150px;
left: 150px;
z-index: 2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box box1"></div>
<div class="box box2"></div>
<div class="box box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
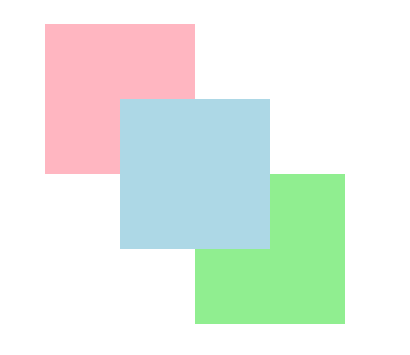
如果z-index為正數,根據以上範例,數字3會在最上方,也就是淺藍色的方塊。
但如果是負數的話就會相反,將z-index 1、2、3改為z-index -1、-2、-3,淺藍色的方塊會顯示在最下方,因為-3為最小數字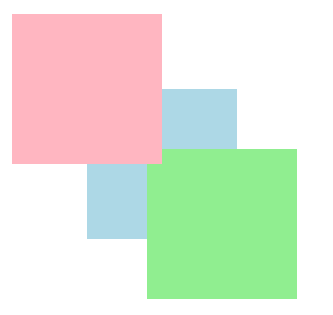
若以上三個方塊的值都改為auto,則會根據內文的先後順序做排序
如果有堆疊的問題就可以運用z-index,不過要記得搭配position做使用呦~~~~
今天的介紹就先到這啦~~~![]()
